Preview
Creation Date
2019
Description
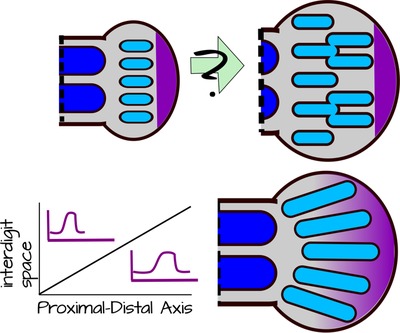
The paddle-shaped autopod should allow for additional condensation formation as it grows. This should lead to additional bones in the distal portion of the autopod or branching of existing condensations (top panel).
Hoxd13 mutants give phenotypes like the top panel suggesting that Hoxd13 modifies the wavelength of the Sox9 condensations. Hoxd13 diffuses from the Apical Ecodermal Ridge and forms a gradient (yellow). Where Hoxd13 levels are high, the wavelength (or interdigit space) is large. Where Hoxd13 levels are low, the wavelength is small. The modulation of Hoxd13 levels and/or its ability to regulate the wavelength results in unbranched digits
Figure originally published in Evolutionary Developmental Biology
Creative Commons License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 4.0 International License.
Keywords
evolution, development, evodevo, limb, digits, fingers, toes, turing, modeling, inhibitor, activator, diffusion, genetics, hox13


